Table of Content
-
- 1.0 Executive Summary 3
-
- 2.0 Introduction 4
-
- 3.0 Environmental Analysis and Audit 4
-
- 3.1 PESTEL Analysis 4
-
- 3.2 SWOT Analysis 5
-
- 3.3 Competition Analysis – Porter’s Five Forces 6
-
- 3.4 Product Offering 8
-
- 3.5 Product Life Cycle 9
-
- 5.0 Marketing Strategy 9
-
- 5.1 Mission 10
-
- 5.2 Marketing Objectives 10
-
- 5.3 Target Markets 10
-
- 5.4 Positioning 10
-
- 5.5 Segmentation 11
-
- 5.6 Ansoff Matrix 11
-
- 5.7 BCG Matrix 11
-
- 5.8 Distribution Strategy 13
-
- 5.9 Marketing Mix 13
-
- 6.0 Financial Analysis 15
-
- 7.0 Implementation Controls 16
-
- 8.0 Corporate Social Responsibility 16
-
- 9.0 Contingency Plan 17
-
- 10.0 Recommendations 17
- References
1.0 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
This is a comprehensive product marketing plan which is aimed at launching virgin laptops and getting it to the end user. The brand name is virgin mobile under the bigger umbrella of virgin group of companies within which virgin laptop will be officially launched and marketed in the United Kingdom (UK). This country has been selected as the target market because Virgin Group is a very successful company within the UK with huge popularity of the brand. The virgin brand is one that is viewed with lots of excitement and many of its products are often most acceptable and successful within the UK (Johnson 2011).
Also, this marketing plan further makes an environmental audit of the selected market with much emphasis on the level of competition within the market. This will then be followed up with an analysis of the marketing strategy for virgin laptops as well include in the structu sensu, that is the relevant monitoring and control measures that will help facilitate and achieve the objectives outlined (Kotler 2009). This marketing plan also includes a concise discourse of financial requirements that will be needed for an effective marketing of Virgin Laptops.
The conclusion will include valuable recommendations which will involve the need for a 10% contingency fund of the total budget that is meant to be invested into the implementation of the marketing plan in order to facilitate and enhance the future penetration of this product into new markets (Johnson, Whittington & Scholes 2011).
2.0 INTRODUCTION
Marketing as defined by the Charter Institutes if Marketing (Charted Institutes of Marketing 2011) is “…the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying consumers’ requirements profitably”. Kotler (Kotler et al 2009: 109) defined a marketing plan as ‘’a written document that summarizes what the marketer has learned about the marketing place and indicates how firm plans to reach its marketing objectives’’.
This plan consists of an environmental audit of the personal computer industry in order to ascertain current position with regards to the retail and banking industry and promotion via different resources such as Internet website directories (i.e. SearchWIZ). The plan employed theoretical frameworks like PESTEL and Porter’s FIVE FORCE. The plan analyzed the product offering and life cycle, marketing strategy, target market, positioning, marketing mix as well as implementation and control. It also made use of strategic clock, BCG matrix and Ansoff Matrix to help evaluate the strategic direction of the company and proposed recommendations.
3.0 ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS AND AUDIT
3.1 PESTEL
The PESTEL analysis of markets aims to evaluate six key features of a new market, namely: a) Political, b) Economical, c) Social, d) Technological, e) Environmental, and f) Legal. According Johnson, Whittington & Scholes (2009:56), this is particularly important as these factors will influence either the success or failure of the new product ‘Virgin range of laptops with windows eight (8)’ in the UK. The following is the PESTEL analysis of Virgin laptops for the UK market:
a) Political and legal factors: The ever increasing focus of both governmental and non-governmental organisations on the environmental impact of high-tech has led to more stringent environmental regulations on the electronic industry such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive (Dalal 2009). Additionally, testing and certification directly affect the supply chains of PC manufacturers which will increase manufacturing cost and lowering profits (Dalal 2009). Other than these key issues, the UK provides a fairly stable political and legal market environment.
b) Economic factors: An increase in VAT from 17.5% to 20% in order to tackle budget deficits will increase corporate spending and an increase in the minimum wage to 15.5% will have a positive effect on the demand (HM Revenue and Customs 2011). However this decline will be followed by a gradual increase in terms of market share from an expected 5.4% in 2009 to 4.4% in 2012 (Gartner 2008).
c) Social: Factors such as education, preference and income levels affect the purchase of laptops within the UK. The UK is a highly literate society and for that matter the usage of laptops is a part of the norm. For instance, within the UK, consumers spending rises during festive periods and demand for laptops will as well rise (Gartner 2009).
d) Technological: Consumer demand for sophisticated gadgets ranging from laptops to phones makes it appropriate the virgin brand to go into laptop production because it offers the sophistication consumers yearn to have.
3.2 SWOT ANALYSIS
The Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats or SWOT analysis is one of the most commonly used tools to evaluate the suitability of markets for the launch of a new product. This framework is used to assess the products’ feasibility in meeting market needs as well as available future courses of action that can be exercised to lead to successful introduction of those products(Johnson, Whittington & Scholes 2009:119). The following is the SWOT analysis of Virgin laptops for the UK market:
a) Strengths: Virgin laptops will meet the expectations of consumers as more emphasis will be placed on the chip that will make processors much smaller and light-weight which is ideal for tablet PCs and Ultrabooks. Thickness – Less than 0.71 inches or 18 millimetres, Weight – Less than 3.1 pounds or 1.41 kg, Battery Life – More than 5 hours, will have Intel’s Rapid start technology and also have flashed based drive for storage (Pinegar 2002).
b) Weaknesses: Virgin mobile, although a part of the prominent Virgin group, is not a major player in the market for laptops and personal computers. It has low brand visibility and low brand loyalty which implies that it will take time for this product to be to penetrate into the market.
c) Opportunities: The virgin brand is one that is most revered within the UK market and for that matter, what customers feel about the virgin brand will be transferred to virgin laptops and it will therefore help in the marketing of this new product. The internet market has matured since the technology sector continuous to grow even in the wake of the financial downturn (Gartner 2009).
d) Threats: The personal computers industry is controlled by five major manufacturers. These are: a) Dell Inc, b) Hewlett-Packard, c) Gateway, d) Lenovo/IBM, and e) Apple Computers with more than 64.2% of market share which will be a threat to this product (Davis 2009).
3.3 COMPETITION ANALYSIS
Michael E. Porter’s five forces model for analysing competition is one of the most widely used market analysis tools. As the name suggests, the model focuses on five key forces that influence the competitive environment of a product. The forces are: a) Entry barriers, b) Threats of substitutes, c) Bargaining power of suppliers, d) Buyers bargaining power, and e) Rivalry from established companies offering the same product. The following is the analysis of market competition for Virgin laptops in the UK based on Porter’s Five Forces model:
a) Threats of new entrants: The cost of production and distribution are the factors that make entrance high (Johnson, Whittington & Scholes 2010). The five main manufacturers are dictating the pace with more than 64.2% of market share (Davis 2009). It implies that new entrants will need to invest so much with low prices in order to compete with market leads (Kotler 2009).
b) Threat of substitute products: The threat of substitute is high because there are several alternatives as phones, tablets and this has resulted in low degree of product differentiation (Davis 2009). With continuous technological innovations, products are developed with similar attributes to laptops with each firm manufacturing product that directly competes with competitors which in the end acts as a substitute (Dalal 2009).
c) The Bargaining power of buyers: Bargaining power of buyer’s is low due to the fact that companies have what is referred to as brand equity and therefore buyers have in-depth know-how about the products available in the market (Dalal 2009).
d) The Bargaining power of suppliers: The microprocessor industry is dominated by Intel technology which holds a market share of over 50 % for the distribution of microprocessors in the market. Consumers usually demand laptops with consistent software and hence as a result of the high degree of product differentiation, changing suppliers becomes difficult which therefore leads to a high supplier power (Anderson 2007) implying moderate bargaining power of suppliers.
e) Intensity of rivalry: There is evidence of strong rivalry among dominant companies within the UK because of the fact that they control more than 64.2% of the UK market share and therefore competition levels are very high within this industry (Anderson 2007).
Figure 1 illustrated the five forces analysis for Virgin laptops in the UK.
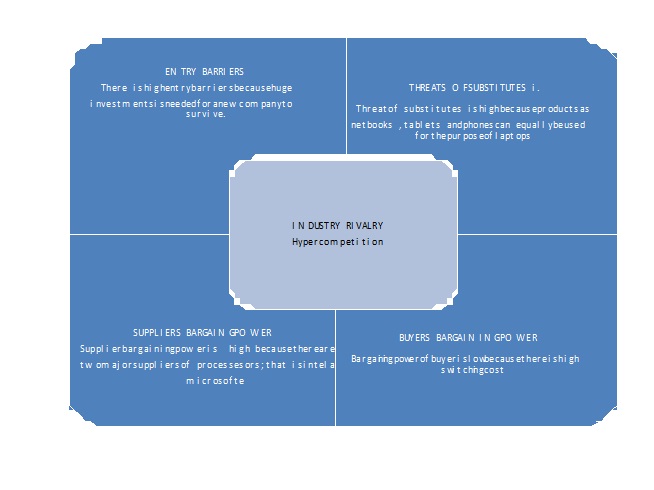
Figure 1
With the above, is conclusive that the UK PC industry is a hyper competitive one and new firms will be successful in such an industry if they have the technical expertise and adequate capital and with brand equity being a matter of need, virgin mobile and virgin group as a whole has what it takes to penetrate into the UK market despite some of these challenges.
3.4 PRODUCT OFFERING
The company will brand and package products to add to a perceived value of customers (Kotler et al 2009:506).By purchasing the product consumers will get the following benefits:
Core Product: Durability, fashionable
Actual Product: Customer satisfaction
Augmented benefit: Ethical standards linked to fair trade products
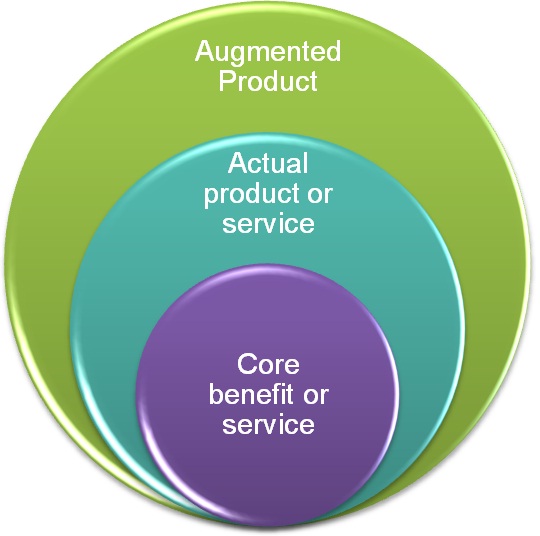
Source: Style communications
Virgin mobile will introduce the following range of laptops:
Processor: 2nd generation Intel® Core™ i5 (windows 8)
i7 processor (2.20 GHz, with Turbo Boost 2.0 up to 3.10 GHz)- (windows 8)
6.0 PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
The life of most products is segregated into five key phases, namely: a) Product development, b) Product introduction, c) Product growth, d) Product maturity, and e) Product decline. The typical product life cycle is depicted in Figure 2:
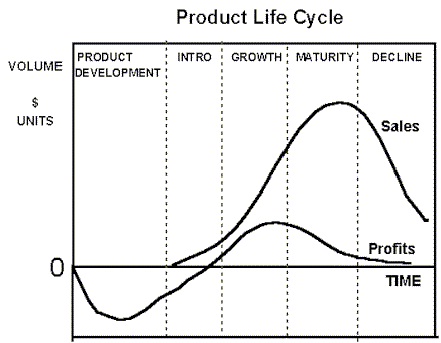
Figure 2
The above diagram shows that virgin ultra – laptops is at the introduction stage but can increase sales revenue by focusing on the brand image of the parent company virgin mobile under virgin group. The product will be at the maturity stage in 3years through rigorous advertisement.
5.0 MARKETING STRATEGY
The marketing strategy offers a direction on the ways of getting a product/service to the consumer which is guided by a routine set of duties and responsibilities. For the effective marketing of Virgin laptops, a pre-emptive strategy will be used whereby a general claim is made but with some assertion that one’s brand is superior (Pickton & Broderick 2005:427).
5.1 MISSION
To offer consumers with intrinsic value of quality durable laptops with greener technology this will come at affordable prices.
5.2 MARKETING OBJECTIVES
By introducing a new product line of virgin laptops, virgin mobile aims to achieve the following objectives:
Short term: To increase brand awareness by 10% which intended to achieve a market share of 5% from 2012 – 2013.
Medium term: Ensure customer satisfaction by 20% through surveys and product development by 2014.
Long term: Launch product in Europe and achieve 6.5% increase in sales between 2014-2015
5.3 TARGET MARKET
As a result of increased computer literacy, the demand for laptops with extra features is rising but will be done on a pilot basis; this product will have its target group as university under-graduate students between the ages of 15-24. There will however be a shift to encompass all university students and professionals in the medium and long-terms respectively.
5.4 POSITIONING
Strategic positioning involves decisions about setting initial prices of a product(s) in response to competitive challenges in the market (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman & Hansen 2009:853). The image is intended to be created as a pre-emptive strategy to help position virgin ultra – laptops as is to position the ‘Virgin Laptops with windows eight (8)’ with emphasis placed on its type not being in the market yet with the features it has and yet prices are comparable to current market leads.
5.5 SEGMENTATION
IT is important to segregate a product’s target market into segments as this allows better focus of marketing and sales effort on those audiences that are most likely to make a purchase of the product. Virgin range of laptops will target university students and professionals since among these groups, laptops have become necessities rather than wants. Research in the light of the economic recession, demand for laptops is on the rise after a fall in 2008 (Garoia 2010).
5.6 ANSOFF MATRIX
Considering Ansoff matrix, Virgin laptops is a new product being introduced in an existing market and therefore categorized under the product development quadrant. The product has a chance of penetrating into the market because of consumers are not only interested in intrinsic value but ethical factors as well (Emerald 2003). With regards to market penetration sales would also be improved by advertisement on brand awareness as well as promotions, discounts, contract laptops, etc. There will be no immediate diversification since the product will need to reach its maturity stage of the product life cycle before diversifying into either related or unrelated products will be considered. Figure 3 highlights the Ansoff Matrix for Virgin laptops for the UK market:
BCG MATRIX
The BCG Matrix was developed by Boston Consulting Group aimed at assessing business potential and evaluating the market environment. Analysing the BCG matrix above shows virgin laptops with windows eight (8) is among the question mark category because it is at the introduction stage of the product life cycle where market share is normally low. This product has a potential of becoming a star at the growth stage. Figure 4 shows the BCG Matrix for Virgin laptops in the UK market:
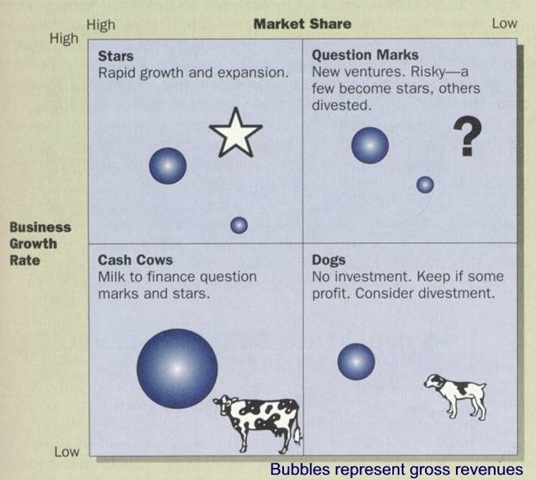
Figure 4
Source: Sooper Tutorials
5.8 DISTRIBUTION STRATEGY
Distribution strategy includes selection and management of channel relationships to deliver value to consumers (Kotler et al 2009:853). Our direct distribution channels consist of our website and Virgin Mobile at your Service, our toll-free customer care centre and the use of a third-party retail distribution channels such as Nextel Stores, Target Stores. A four – party retail distribution channel also include Amazon.com will place product within their stores to promote sales (Lynch 2008).
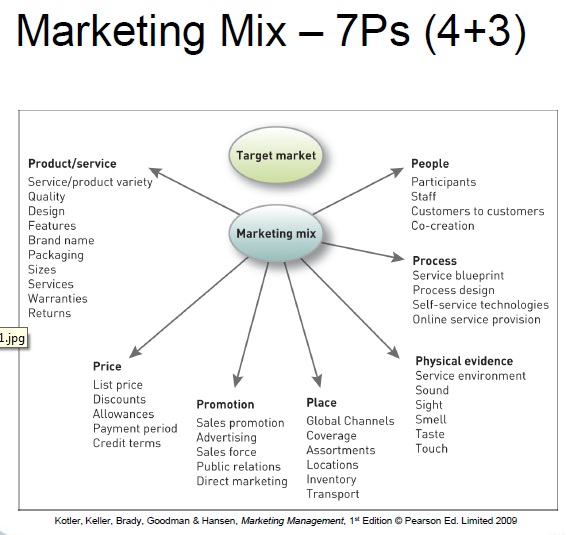
5.9 MARKETING MIX
PRODUCT: Virgin ultra – laptops will be made-up of Chip that will make processors much smaller and light-weight which is ideal for tablet PCs and Ultrabooks. Thickness – Less than 0.71 inches or 18 millimetres, Weight – Less than 3.1 pounds or 1.41 kg, Battery Life – More than 5 hours, will have Intel’s Rapid start technology and also have flashed based drive for storage with windows eight (8) which is not available in the market presently. This product is also manufactured to be environmentally friendly. This will be very appropriate for the current laptop consumer market.
PRICING: Prices will be earmarked to meet middle income earners purchasing levels since most of UK population consider themselves middle or working class people (BBC 2009). This marketing plan will use customer based pricing approach since we aim to penetrate into the market by persuading consumers from switching to virgin range of laptops;
Prices:
1 Virgin ultra-laptop 14” (windows eight) – £650
2 Virgin ultra-laptop 15.6” (windows eight) – £700
PLACE: This product will be introduced in UK as a test market which will be followed with a survey to ascertain customer satisfaction and the feedback will influence the launch of the product in the European economies in the long term.
PROMOTION: Virgin mobile under the virgin group is a strong brand in the industry but to further increase consumer awareness of its new product line ’virgin laptops’, raise awareness about the new brand under the bigger umbrella of the well-recognised virgin brand, advertisement campaigns will be staged via online and offline marketing communication channels. It also includes advertising on websites as direct communication through blogging Google, yahoo, and gum tree etc. (Kotler, Keller, Brady, Goodman & Hansen 2009:711).
PEOPLE & PROCESS: Virgin mobile has a well-developed marketing department. However, an introduction of a new product requires training on departmental basis to equip workers with the necessary information on the new product. The product will be marketed through existing marketing channels as well as online. A simplified IT approach will be used where a low-touch uniform infrastructure spanning the desktop to the data centre will be employed to the measurement of operational efficiency (Dell 2012).
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE: Through billboards, magazines and live TV commercials showcasing the new range of laptops, consumers will get to know the quality and durability of the virgin laptops before the launch of the product in the UK.
6.0 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS
Price penetration strategy as mentioned in the marketing mix will be employed with an estimated average price pegged at £550 and £6500 prices respectively. An average variable cost is estimated at £400 and £450 respectively. The initial fixed cost for the production of the virgin range of laptops is estimated at £5,000,000 and £6,000,000 respectively which will total £11,000,000. Virgin laptops intend to start making profit from the 2nd year when the product break even with an increased sale volume of £3,000,000.
7.0 IMPLEMENTATION AND CONTROLS
…